Librewolf is an increasingly popular browser in the privacy-conscious community, often cited as a safer alternative to mainstream browsers. Sometimes it even gets compared to what many consider to be the best privacy focused mainstream browser: Brave. But that begs the question, is Librewolf truly better than the rest and worth switching to? Let’s explore.
Librewolf At A Glance
What is Librewolf?
Librewolf is an open-source, privacy-focused web browser based on Mozilla Firefox. Unlike Firefox, which comes with some telemetry and tracking features enabled by default, Librewolf eliminates these elements to prioritize user privacy. It is independently maintained by a community of developers who ensure that the browser adheres to strict privacy standards.
Librewolf incorporates built-in tools for enhanced security, such as uBlock Origin for ad and tracker blocking, and is configured to operate without connecting to Mozilla servers. It also disables WebRTC by default to prevent IP leaks, making it a favored choice for those using VPNs. Additionally, it doesn’t require users to create an account or log in, further reinforcing its privacy-first approach.
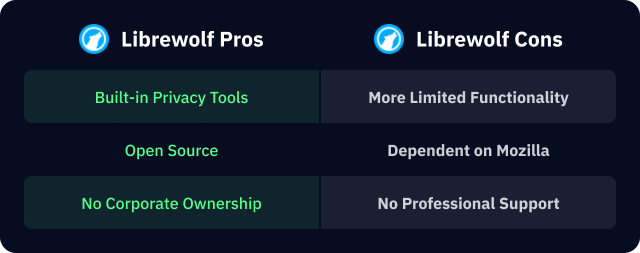
While Librewolf offers fewer features than mainstream browsers, this simplicity aligns with its goal of minimizing attack surfaces and tracking risks. Its open-source nature ensures transparency, allowing users to review and verify its code.
Is Librewolf a Safe Browser?
Yes, Librewolf is generally considered a safe browser, particularly for privacy-conscious users. However, safety is multifaceted, involving elements like privacy protection, resistance to cyberattacks, and secure browsing practices.
By disabling telemetry and blocking trackers, Librewolf significantly reduces the risk of data collection. Its pre-installed privacy tools, like HTTPS-Only Mode, ensure encrypted connections to websites, further safeguarding user data. Additionally, its compatibility with VPNs and proxy settings enhances security by masking your IP address and encrypting your online activity.
However, no browser is completely immune to vulnerabilities. Librewolf relies on Mozilla’s Firefox engine, so any security flaws in Firefox could potentially affect Librewolf. Regular updates from the Librewolf team mitigate this risk, but users must ensure they keep the browser up-to-date.
Librewolf also lacks certain features like sandboxing and site isolation found in some other browsers, which could affect its resilience against advanced threats. Thus, while it excels in privacy, its security framework isn’t invincible.
How a Secure Browser Works
A secure browser protects users from online threats while maintaining a high level of privacy. Core functionalities include blocking trackers, encrypting communications, and defending against malware and phishing attempts.
Key features of a secure browser include:
- Tracker and Ad Blocking: By preventing third-party scripts from running, secure browsers protect users from invasive tracking and reduce the risk of malicious advertisements.
- Encrypted Connections: HTTPS-Only Mode ensures all communication between the browser and websites is encrypted, safeguarding sensitive data like passwords and credit card information.
- Sandboxing: Isolating browser processes from the operating system prevents malicious sites from accessing sensitive system data.
- Regular Updates: Frequent updates patch vulnerabilities and strengthen defense mechanisms.
Secure browsing also depends on user behavior, such as avoiding suspicious links and keeping plugins and extensions minimal to reduce attack surfaces.
Security and Privacy are Two Sides of the Same Coin
While security and privacy are interrelated, they are not identical. Privacy concerns protecting user data from being collected, tracked, or shared, while security focuses on protecting systems from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
For example, a browser might encrypt your online activity to enhance security but still collect your data for advertising purposes, which compromises privacy. Conversely, a privacy-focused browser might block trackers but lack robust defenses against malware.
Librewolf emphasizes privacy by disabling telemetry and removing unnecessary data collection features. While it offers decent security measures, users seeking comprehensive protection must combine it with tools like antivirus software and a reliable VPN.
How Does Librewolf Compare to Other Secure Browsers?
Since you’re probably going to be using a web browser almost daily if not everyday, you must consider all the options available to you. The browser landscape isn't an outright monopoly, but Google wields significant influence due to its dominance over the Chromium web engine.
Although Chromium is open source, most major browsers—except Firefox—rely on it as their foundation. This reliance ties these browsers to Google’s standards, including the new Manifest V3 (MV3) framework for web extensions. MV3 introduces restrictions that, while framed as security enhancements, also limit the effectiveness of ad blockers and privacy tools. This shift ultimately benefits Google by ensuring more ads and trackers make their way into your browsing experience, thereby increasing their ad revenue.
Librewolf vs Google Chrome
Google Chrome dominates the browser market but falls short in privacy compared to Librewolf. Chrome collects vast amounts of user data, including browsing history and personal preferences, to fuel Google’s advertising algorithms.
Librewolf, by contrast, disables all forms of tracking and telemetry, ensuring that user data remains private. It also comes with pre-installed privacy tools, while Chrome requires users to manually add extensions like uBlock Origin or Privacy Badger.
From a security perspective, Chrome is robust, offering advanced features like sandboxing and frequent updates. However, its privacy trade-offs make it unsuitable for those prioritizing anonymity.
Librewolf vs Brave
Brave is another popular privacy-focused browser, often compared to Librewolf. While both prioritize user privacy, their approaches differ.
Brave integrates privacy tools like a built-in ad blocker and shields against fingerprinting. However, it also includes features like Brave Rewards, which some criticize as undermining its privacy-first stance since it can be linked back to your account. Brave is also partially funded by cryptocurrency initiatives, which might not appeal to all users.
Librewolf avoids these complexities by sticking to its minimalist, telemetry-free design. It doesn’t include optional features that could potentially introduce vulnerabilities or confuse users.
In terms of security, Brave’s integration of HTTPS Everywhere and frequent updates make it a strong contender, but Librewolf’s simplicity and transparency give it an edge for users who value straightforward, uncompromising privacy.
Librewolf vs Firefox
Since Librewolf is based on Firefox, the two browsers share many similarities. However, Librewolf is essentially a privacy-enhanced version of Firefox, with telemetry disabled and privacy settings preconfigured.
Firefox, while privacy-conscious compared to browsers like Chrome, still collects some data by default. Users can adjust its settings to enhance privacy, but this requires manual effort. Librewolf removes this burden by offering a secure configuration out of the box.
In terms of features, Firefox supports a broader ecosystem of extensions and customization options, while Librewolf intentionally limits certain functionalities to reduce attack surfaces.
Librewolf vs Safari
Safari, Apple’s default browser, is known for its strong privacy features, including Intelligent Tracking Prevention. However, its reliance on Apple’s ecosystem limits its compatibility with non-Apple devices.
Librewolf surpasses Safari in transparency, as it is open-source and doesn’t tie users to a specific platform. Safari collects some user data for Apple’s services, which might deter privacy enthusiasts. Moreover, Librewolf’s built-in tracker blocking is more aggressive than Safari’s.
Safari benefits from Apple’s robust security infrastructure, including sandboxing and protection against malicious websites. Librewolf, while solid in privacy, may not match Safari’s overall security measures.
Librewolf vs Tor
The Tor browser is the gold standard for anonymity, using the Tor network to encrypt traffic and route it through multiple nodes. Librewolf, while privacy-focused, does not offer the same level of anonymity.
For general browsing, Librewolf is faster and less resource-intensive than Tor. It’s also more user-friendly, making it suitable for everyday use. However, for activities requiring maximum anonymity, such as accessing the dark web, Tor is unmatched.
Librewolf vs Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge, based on Chromium, offers improved privacy features compared to its predecessor, Internet Explorer. However, like Chrome, it collects significant user data for Microsoft services.
Librewolf, with its anti-tracking tools and telemetry-free design, is a clear winner in privacy. Edge’s integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem might be convenient for some users, but it’s a drawback for those prioritizing independence and transparency.
Key Considerations Before Using Librewolf
While Librewolf is an excellent choice for privacy enthusiasts, it is not without its limitations:
- Performance: Some users report slower performance compared to mainstream browsers, especially on resource-heavy websites.
- Limited Features: By stripping down Firefox, Librewolf sacrifices some functionality, which may frustrate users who rely on advanced features.
- Dependency on Firefox: As Librewolf is based on Firefox, it inherits any vulnerabilities or flaws present in Mozilla’s codebase.
- Niche Audience: Librewolf’s focus on privacy might not appeal to casual users, and its smaller community means fewer extensions and less support compared to browsers like Chrome or Firefox.
- Design Vulnerabilities: While LibreWolf prioritizes user privacy, there are still some weaknesses to be aware of:
- Browser fingerprinting protection is not enabled, unlike Tor Browser's resistance techniques.
- LibreWolf relies on central authorities for TLS certificates, which may leave room for improvement in anti-tracking and traffic analysis protections.
Who Should Use LibreWolf?
LibreWolf is ideal for users who prioritize security and privacy above all else. However, it requires a willingness to make some compromises in terms of convenience:
- Technical Inclination: LibreWolf requires technical expertise to configure site permissions and toggle protection settings. Things will likely not work out of the box as seamlessly as they do with Firefox or Chrome.
- Casual Users May Struggle: For those who value seamless browsing experiences without configuration, LibreWolf may be frustrating at times.
Lock Down Your Connection With A VPN
By first connecting to Windscribe VPN, and then to Librewolf, you're already ahead of the game. Adding Windscribe as an intermediary layer to your connection means your data is encrypted before you even open up the browser.
Final Considerations Before Choosing LibreWolf
Before deciding on LibreWolf, reflect on the following. You may find this may make or break your decision process:
- Frequent Updates: LibreWolf receives updates less frequently than mainstream browsers like Firefox. This might cause issues for users relying on the latest web technologies and standards.
- Support: While there is a community of users and contributors supporting LibreWolf, it may not offer the same level of support as more widely used browsers.
Conclusion: Librewolf + Windscribe Is The Way
Librewolf is a safe and privacy-respecting browser ideal for users seeking a secure alternative to mainstream options. While it has limitations, its minimalist and transparent approach to privacy makes it a standout choice for the privacy-conscious community. For comprehensive security, pairing Librewolf with other privacy tools like Windscribe is a wise choice.









